C Sharp Read Text File to Array and Get Average
An assortment is a group of like-typed variables that are referred to past a mutual proper name. And each information item is called an element of the array. The data types of the elements may exist any valid information type like char, int, float, etc. and the elements are stored in a contiguous location. Length of the array specifies the number of elements present in the array. In C# the allotment of memory for the arrays is done dynamically. And arrays are kinds of objects, therefore it is like shooting fish in a barrel to find their size using the predefined functions. The variables in the array are ordered and each has an alphabetize beginning from 0. Arrays in C# work differently than they do in C/C++.
Important Points to Recollect About Arrays in C#
- In C#, all arrays are dynamically allocated.
- Since arrays are objects in C#, we can find their length using member length. This is different from C/C++ where nosotros find length using sizeof operator.
- A C# array variable can besides be declared similar other variables with [] afterwards the data type.
- The variables in the assortment are ordered and each has an index offset from 0.
- C# assortment is an object of base type System.Array.
- Default values of numeric array and reference blazon elements are gear up to exist respectively zero and null.
- A jagged array elements are reference types and are initialized to null.
- Array elements can be of whatever type, including an array type.
- Array types are reference types which are derived from the abstruse base of operations type Assortment. These types implement IEnumerable and for it, they apply foreach iteration on all arrays in C#.
The array has can contain archaic data types every bit well as objects of a form depending on the definition of an assortment. Whenever use primitives data types, the actual values take to be stored in contiguous memory locations. In the case of objects of a class, the actual objects are stored in the heap segment.
The following figure shows how array stores values sequentially :
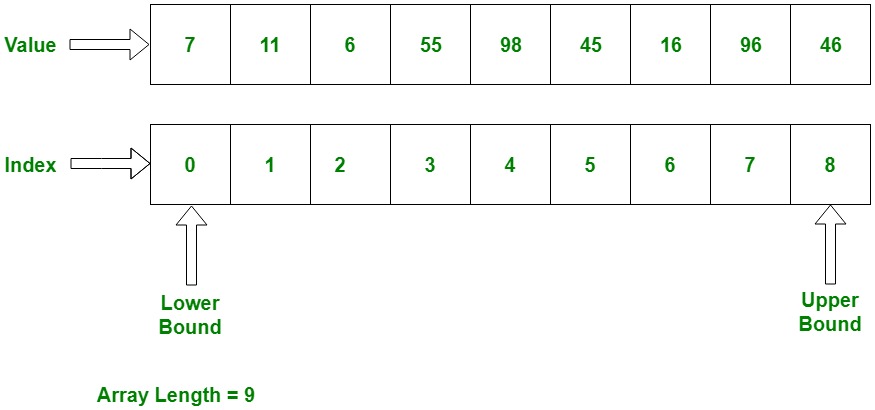
Explanation :
The alphabetize is starting from 0, which stores value. we can likewise shop a fixed number of values in an assortment. Assortment index is to be increased by 1 in sequence whenever its not reach the array size.
Array Declaration
Syntax :
< Data Blazon > [ ] < Name_Array >
Here,
< Data Type > : Information technology ascertain the element type of the array.
[ ] : Information technology ascertain the size of the array.
< Name_Array > : It is the Name of array.
Example :
int[] x; // can store int values string[] s; // tin can store cord values double[] d; // can store double values Student[] stud1; // can store instances of Student grade which is custom grade
Note : Merely Declaration of an assortment doesn't allocate retentiveness to the array. For that array must exist initialized.
Array Initialization
As said earlier, an array is a reference type so the new keyword used to create an example of the array. We tin can assign initialize individual array elements, with the help of the index.
Syntax :
blazon [ ] < Name_Array > = new < datatype > [size];
Hither, type specifies the type of data being allocated, size specifies the number of elements in the array, and Name_Array is the proper noun of an array variable. And new will allocate retentiveness to an array according to its size.
Examples : To Show Unlike means for the Assortment Declaration and Initialization
Case 1 :
// defining array with size 5. // But not assigns values int[] intArray1 = new int[v];
The above statement declares & initializes int type array that can store five int values. The array size is specified in foursquare brackets([]).
Example 2 :
// defining array with size 5 and assigning // values at the aforementioned time int[] intArray2 = new int[5]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; The above argument is the same as, but it assigns values to each index in {}.
Example 3 :
// defining array with v elements which // indicates the size of an array int[] intArray3 = {i, 2, three, 4, five}; In the above statement, the value of the array is direct initialized without taking its size. So, array size volition automatically exist the number of values which is directly taken.
Initialization of an Array after Proclamation
Arrays tin can be initialized after the declaration. It is not necessary to declare and initialize at the same time using the new keyword. However, Initializing an Array afterwards the announcement, it must be initialized with the new keyword. It can't be initialized past only assigning values.
Example :
// Declaration of the array
cord[] str1, str2;// Initialization of array
str1 = new string[5]{ "Element 1", "Element 2", "Chemical element three", "Element iv", "Element 5" };str2 = new string[5]{ "Element 1", "Element two", "Element iii", "Element 4", "Chemical element 5" };
Annotation : Initialization without giving size is not valid in C#. It volition give a compile-time error.
Instance : Wrong Declaration for initializing an array
// compile-time error: must give size of an array
int[] intArray = new int[];// error : incorrect initialization of an assortment
string[] str1;
str1 = {"Chemical element 1", "Element 2", "Chemical element iii", "Chemical element iv" };
Accessing Assortment Elements
At the time of initialization, we tin can assign the value. Just, we can likewise assign the value of the array using its index randomly afterwards the declaration and initialization. We tin can access an array value through indexing, placed index of the element within foursquare brackets with the array name
Example :
//declares & initializes int blazon assortment int[] intArray = new int[v]; // assign the value 10 in array on its index 0 intArray[0] = 10; // assign the value thirty in array on its alphabetize two intArray[2] = xxx; // assign the value 20 in array on its index one intArray[1] = 20; // assign the value 50 in array on its index 4 intArray[4] = fifty; // assign the value twoscore in array on its index 3 intArray[three] = 40; // Accessing array elements using index intArray[0]; //returns 10 intArray[2]; //returns 30
Implementation : Accessing Array elements using different loops
using Arrangement;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
course GFG {
public static void Main()
{
int [] intArray;
intArray = new int [5];
intArray[0] = 10;
intArray[1] = twenty;
intArray[2] = 30;
intArray[iii] = xl;
intArray[4] = 50;
Console.Write( "For loop :" );
for ( int i = 0; i < intArray.Length; i++)
Console.Write( " " + intArray[i]);
Console.WriteLine( "" );
Console.Write( "For-each loop :" );
foreach ( int i in intArray)
Panel.Write( " " + i);
Panel.WriteLine( "" );
Console.Write( "while loop :" );
int j = 0;
while (j < intArray.Length) {
Console.Write( " " + intArray[j]);
j++;
}
Panel.WriteLine( "" );
Console.Write( "Exercise-while loop :" );
int one thousand = 0;
do
{
Panel.Write( " " + intArray[m]);
g++;
} while (1000 < intArray.Length);
}
}
}
Output :
For loop : ten xx xxx 40 50 For-each loop : 10 20 30 40 fifty while loop : 10 xx 30 40 50 Practise-while loop : 10 20 30 40 l
One Dimensional Array
In this array contains but 1 row for storing the values. All values of this assortment are stored contiguously starting from 0 to the array size. For example, declaring a single-dimensional array of five integers :
int[] arrayint = new int[5];
The above array contains the elements from arrayint[0] to arrayint[four]. Here, the new operator has to create the array and also initialize its element by their default values. Above instance, all elements are initialized past zero, Considering it is the int type.
Example :
using Organisation;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class GFG {
public static void Main()
{
string [] weekDays;
weekDays = new string [] { "Sun" , "Mon" , "Tue" , "Wed" ,
"Thu" , "Fri" , "Sabbatum" };
foreach ( cord day in weekDays)
Console.Write(day + " " );
}
}
}
Output :
Sun Monday Tue Wednesday Thu Fri Saturday
Multidimensional Arrays
The multi-dimensional assortment contains more than one row to store the values. It is also known as a Rectangular Assortment in C# because it's each row length is same. Information technology can be a 2D-array or 3D-array or more. To storing and accessing the values of the array, one required the nested loop. The multi-dimensional array declaration, initialization and accessing is as follows :
// creates a two-dimensional array of // iv rows and ii columns. int[, ] intarray = new int[4, 2]; //creates an array of three dimensions, 4, 2, and 3 int[,, ] intarray1 = new int[4, ii, 3];
Example :
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class GFG {
public static void Main()
{
int [, ] intarray = new int [, ] { { 1, ii },
{ 3, 4 },
{ v, half dozen },
{ seven, 8 } };
int [, ] intarray_d = new int [4, 2] { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6 }, { vii, viii } };
string [, ] str = new string [4, 2] { { "one" , "two" },
{ "three" , "four" },
{ "5" , "six" },
{ "seven" , "8" } };
int [,, ] intarray3D = new int [,, ] { { { 1, ii, 3 },
{ 4, v, half-dozen } },
{ { 7, eight, ix },
{ 10, 11, 12 } } };
int [,, ] intarray3Dd = new int [2, 2, 3] { { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, half-dozen } },
{ { 7, viii, nine },
{ ten, 11, 12 } } };
Panel.WriteLine( "2DArray[0][0] : " + intarray[0, 0]);
Panel.WriteLine( "2DArray[0][1] : " + intarray[0, i]);
Panel.WriteLine( "2DArray[1][1] : " + intarray[1, one]);
Console.WriteLine( "2DArray[2][0] " + intarray[2, 0]);
Console.WriteLine( "2DArray[1][one] (other) : "
+ intarray_d[one, 1]);
Console.WriteLine( "2DArray[i][0] (other)"
+ intarray_d[1, 0]);
Console.WriteLine( "3DArray[1][0][1] : "
+ intarray3D[1, 0, 1]);
Console.WriteLine( "3DArray[one][one][2] : "
+ intarray3D[1, 1, ii]);
Console.WriteLine( "3DArray[0][1][1] (other): "
+ intarray3Dd[0, i, 1]);
Console.WriteLine( "3DArray[i][0][2] (other): "
+ intarray3Dd[1, 0, ii]);
Console.WriteLine( "To Cord chemical element" );
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for ( int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
Console.Write(str[i, j] + " " );
}
}
}
Output :
2DArray[0][0] : 1 2DArray[0][1] : 2 2DArray[1][1] : four 2DArray[2][0] 5 2DArray[1][one] (other) : 4 2DArray[1][0] (other)three 3DArray[one][0][i] : viii 3DArray[1][1][2] : 12 3DArray[0][one][1] (other): v 3DArray[1][0][2] (other): nine To String element 1 two three iv five vi seven 8
Jagged Arrays
An array whose elements are arrays is known as Jagged arrays it means "array of arrays". The jagged assortment elements may be of different dimensions and sizes. Below are the examples to show how to declare, initialize, and access the jagged arrays.
Example :
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class GFG {
public static void Main()
{
int [][] arr = new int [two][];
arr[0] = new int [5] { 1, 3, 5, vii, 9 };
arr[ane] = new int [4] { two, 4, vi, 8 };
int [][] arr1 = { new int [] { ane, 3, 5, 7, nine },
new int [] { two, 4, vi, 8 } };
for ( int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
System.Console.Write( "Chemical element [" + i + "] Array: " );
for ( int j = 0; j < arr[i].Length; j++)
Console.Write(arr[i][j] + " " );
Console.WriteLine();
}
Panel.WriteLine( "Another Assortment" );
for ( int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++)
{
System.Panel.Write( "Element [" + i + "] Assortment: " );
for ( int j = 0; j < arr1[i].Length; j++)
Console.Write(arr1[i][j] + " " );
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
Output :
Element [0] Assortment: 1 3 5 7 ix Element [1] Assortment: ii iv 6 8 Another Assortment Element [0] Assortment: 1 3 5 7 9 Chemical element [ane] Array: 2 4 half dozen 8
It'due south possible to mix jagged and multidimensional arrays. The jagged array is an assortment of arrays, and therefore its elements are reference types and are initialized to null.
Example : To Declare and initialization of a single-dimensional jagged array which contains three ii-dimensional array elements of different sizes.
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
form GFG {
public static void Primary()
{
int [][, ] arr = new int [3][, ] { new int [, ] {{one, 3}, {5, vii}},
new int [, ] {{0, two}, {4, 6}, {8, x}},
new int [, ] {{11, 22}, {99, 88}, {0, ix}}};
for ( int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
int x = 0;
for ( int j = 0; j < arr[i].GetLength(10); j++)
{
for ( int chiliad = 0; g < arr[j].Rank; one thousand++)
Console.Write( " arr[" + i + "][" + j + ", " + k + "]:"
+ arr[i][j, k] + " " );
Console.WriteLine();
}
ten++;
Panel.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
Output :
arr[0][0, 0]:1 arr[0][0, 1]:iii arr[0][1, 0]:5 arr[0][1, 1]:7 arr[1][0, 0]:0 arr[ane][0, 1]:2 arr[1][1, 0]:4 arr[1][one, ane]:6 arr[ane][ii, 0]:8 arr[one][2, 1]:10 arr[2][0, 0]:11 arr[2][0, 1]:22 arr[2][1, 0]:99 arr[2][i, 1]:88 arr[two][2, 0]:0 arr[ii][2, ane]:9
Points To Retrieve :
- GetLength(int): returns the number of elements in the starting time dimension of the Array.
- When using jagged arrays exist rubber as if the index does not exist then it volition throw exception which is IndexOutOfRange.
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/c-sharp-arrays/
0 Response to "C Sharp Read Text File to Array and Get Average"
Enregistrer un commentaire